Political Alignment of the Federal Government

Germany is a democratic federal state where elections Elections Every four years, the parties stand in the general elections to the Bundestag. Traditionally, the turn-out is high in Germany, and following a high in the 1970s, when the turn-out was over 90 percent, since reunification it has been around 80 percent. 76.6 per cent of eligible voters took part… Read more › at national and state levels often cause changes in government. The Bundestag The Bundestag The Bundestag is made up of the elected representatives of the German people. In principle elections to the Bundestag are proportionally representative, with each party’s share of the vote in the election reflecting the number of seats it occupies in the parliament. But the electoral system also… Read more › elections of September 2021 resulted in a coalition between the SPD, Greens and FDP led by Federal Chancellor Federal chancellor The Federal Chancellor is the only member of the Federal Government to be elected. The constitution empowers him to personally choose his ministers, who head the most important political authorities. Moreover it is the Chancellor who determines the number of ministries and their responsibilities… Read more › Olaf Scholz. This replaced the previous CDU/CSU and SPD coalition led by Chancellor Angela Merkel.
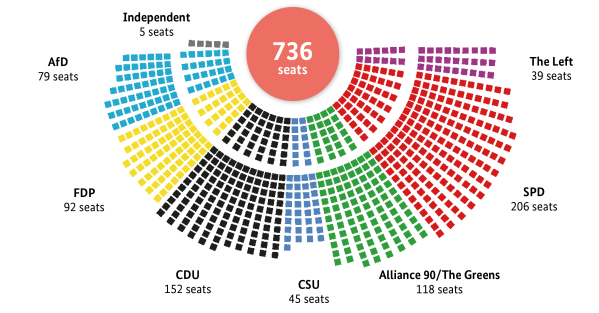
Allocation of seats in the Bundestag
On 8 December 2021, the SPD politician Olaf Scholz was elected by the German Bundestag to serve as the 9th Chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany. He succeeded Angela Merkel of the CDU, who had governed Germany for 16 years. The government that has held office since then is formed of three parties: the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD), Alliance 90/The Greens, and the Free Democratic Party (FDP). Robert Habeck is Vice Chancellor and also serves as Minister for Economic Affairs and Climate Action. Annalena Baerbock is the Foreign Minister. Habeck and Baerbock are both members of the Alliance 90/The Greens parliamentary group. Christian Lindner of the FDP is the Federal Finance Minister. The Federal Cabinet consists of 15 ministers and the Head of the Chancellery.
Following the Bundestag The Bundestag The Bundestag is made up of the elected representatives of the German people. In principle elections to the Bundestag are proportionally representative, with each party’s share of the vote in the election reflecting the number of seats it occupies in the parliament. But the electoral system also… Read more › election of 26 September 2021, the three governing parties hold 416 out of the 736 seats in the German Bundestag. The opposition in the Bundestag is formed by the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) and the Christian Social Union (CSU), which join forces as the Union, along with The Left and the Alternative for Germany (AfD). A three-way coalition of the SPD, Alliance 90/The Greens and the FDP is a first for Germany, as previous governments had almost always been two-party alliances. The Union and the SPD formed the government until the handover of power in 2021.
Coalition Agreement priorities
The coalition agreement forms the basis for how the governing parties work together. The SPD, Alliance 90/The Greens and the FDP signed the agreement before electing Scholz as Federal Chancellor Federal chancellor The Federal Chancellor is the only member of the Federal Government to be elected. The constitution empowers him to personally choose his ministers, who head the most important political authorities. Moreover it is the Chancellor who determines the number of ministries and their responsibilities… Read more › . Under the headline “Daring to make progress – alliance for freedom, justice and sustainability”, the agreement outlines the key priorities for the Federal Government Federal Government The Federal Government and cabinet is made up of the Federal Chancellor and the Federal Ministers. While the Chancellor holds the power to issue directives, the ministers have departmental powers, meaning that they independently run their respective ministries in the framework of those directives… Read more › in the four years of this parliamentary legislative period. The next Bundestag elections Elections Every four years, the parties stand in the general elections to the Bundestag. Traditionally, the turn-out is high in Germany, and following a high in the 1970s, when the turn-out was over 90 percent, since reunification it has been around 80 percent. 76.6 per cent of eligible voters took part… Read more › are scheduled for Autumn 2025.
Making Germany a climate-neutral Industrial Country by 2045
One key policy area for the Federal Government Federal Government The Federal Government and cabinet is made up of the Federal Chancellor and the Federal Ministers. While the Chancellor holds the power to issue directives, the ministers have departmental powers, meaning that they independently run their respective ministries in the framework of those directives… Read more › concerns transforming Germany’s industry and economy to make the country climate-neutral by 2045. In his first government statement, Federal Chancellor Federal chancellor The Federal Chancellor is the only member of the Federal Government to be elected. The constitution empowers him to personally choose his ministers, who head the most important political authorities. Moreover it is the Chancellor who determines the number of ministries and their responsibilities… Read more › Scholz described the “greatest transformation of our industry and economy for at least 100 years.” Specifically the government is undertaking a swift and comprehensive energy transformation. According to the coalition agreement, 80% of Germany’s electricity will come from renewable sources by 2030.
The government has also identified a need for substantial action given the challenges posed by globalisation and digitalisation. At the same time, Scholz promised that, “We will create new confidence through this transformation and will ensure security during this transformation.” The Federal Government's commitments include raising Germany’s legal minimum wage to 12 euros. It also pledged to provide guaranteed training places for young people and stable pensions. In order to protect Germany’s strength as an innovator, over three 3% of GDP is directed to research and development each year. The aim is for this to rise to at least 3.5% of all state expenditure by 2025. Germany intends to make itself even more attractive for skilled professionals from abroad. One element of this is developing modern immigration Immigration As early as the 19th century Germany attracted a large number of immigrants and since the 1950s has emerged as the European country with the largest immigrant population. In 1950, there were about 500,000 foreigners in Germany, accounting for a mere one percent or so of the population. This has… Read more › laws.
The Federal Government also plans to create Germany’s first-ever comprehensive National Security Strategy. Its priorities will include protection from violence and war and promoting the resilience of democracy. The Federal Foreign Office has initiated consultations with civil society groups on how the strategy will be initiated.
Zeitenwende nach russischem Überfall auf die Ukraine
Der völkerrechtswidrige Angriff Russlands auf die Ukraine am 24. Februar 2022 markiert für Bundeskanzler Scholz eine „Zeitenwende“ für Europa und auch für die deutsche Politik. Er kündigte kurz nach dem Überfall unter anderem ein Sondervermögen in Höhe von 100 Milliarden Euro Euro The euro is the currency of the European Monetary Union and after the US dollar the second most important member of the international currency system. Together with the national central banks, the European Central Bank (ECB), headquartered in Frankfurt/Main, is responsible for monetary policy… Read more › zur Stärkung der Bundeswehr an. Deutschland gehört zu den wichtigsten Verbündeten der Ukraine und ist nach den USA das zweitgrößte Geberland – bei humanitärer Unterstützung, direkten Zahlungen oder mit Waffen. Mehr als eine Million Geflüchtete, vor allem Frauen und Kinder, fanden Schutz in Deutschland.
A trusted partner around the world
Germany’s tradition of close cooperation with its partners around the world forms the basis of the
Federal Government
Federal Government
The Federal Government and cabinet is made up of the Federal Chancellor and the Federal Ministers. While the Chancellor holds the power to issue directives, the ministers have departmental powers, meaning that they independently run their respective ministries in the framework of those directives…
Read more ›
’s foreign policy. According to the coalition agreement, “the only way to overcome the great challenges of our age is through international cooperation and as a partner within a strong European
Union.” “A commitment to peace, freedom,
human rights
Human rights
The respect and strengthening of human rights worldwide are a cornerstone of German Federal Government policy. Together with its EU partners it is committed to protecting and continually advancing human rights standards throughout the world. This occurs in close collaboration with the institutions…
Read more ›
, democracy, the rule of law, and sustainability is for us an essential element of a successful and credible foreign policy.”


