What does federalism mean in Germany?

Germany is a federation. The federal government Federal Government The Federal Government and cabinet is made up of the Federal Chancellor and the Federal Ministers. While the Chancellor holds the power to issue directives, the ministers have departmental powers, meaning that they independently run their respective ministries in the framework of those directives… Read more › and the 16 federal states Federal states Germany is a federal state. Both the central federal government and the 16 federal states have independent areas of jurisdiction. The government in Berlin is responsible for foreign policy, European policy, defense, justice, employment, social affairs, tax and health. The federal states are… Read more › each have their own decision-making powers. The individual states are responsible for decisions relating to internal security, schools and higher education, culture and municipal administration. At the same time, the state governments implement not only their own laws but also those issued by the federal government. The governments of the states are directly involved in the federal legislative process through their representatives in the Bundesrat The Bundesrat The Bundesrat represents the federal states and alongside the Bundestag is a form of Second Chamber. It is obliged to deliberate on each federal law. As the chamber of the federal states, the Bundesrat has the same function as those Second Chambers in other federal states that are mostly referred… Read more › (the second chamber of parliament).
Why does Germany have a federal system?
Federalism in Germany is more than just a system of government. Deeply rooted in tradition, it reflects the country’s decentralised cultural and economic structure. Above and beyond their political function, the federal states Federal states Germany is a federal state. Both the central federal government and the 16 federal states have independent areas of jurisdiction. The government in Berlin is responsible for foreign policy, European policy, defense, justice, employment, social affairs, tax and health. The federal states are… Read more › also embody distinct regional identities. Their key role was enshrined in the Basic Law The Basic Law The Basic Law determines that Germany is a constitutional state: All state authorities are subject to judicial control. Section 1 of the Basic Law is of particular relevance. It stipulates that respect for human dignity is the most important aspect of the constitution: “Human dignity shall be… Read more › in 1949.
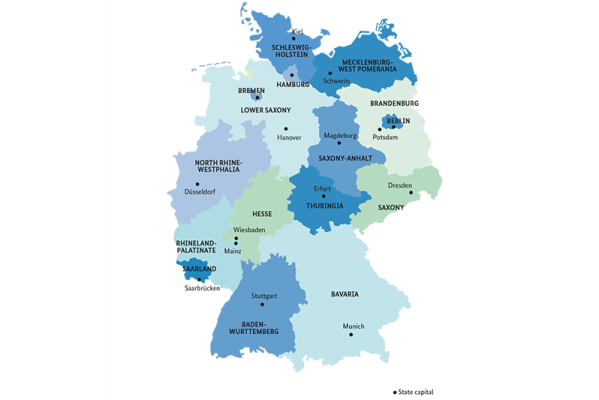
How many federal states does Germany have?
Since reunification in 1990, Germany has consisted of 16 federal states Federal states Germany is a federal state. Both the central federal government and the 16 federal states have independent areas of jurisdiction. The government in Berlin is responsible for foreign policy, European policy, defense, justice, employment, social affairs, tax and health. The federal states are… Read more › ; five new states were established when the German Democratic Republic (GDR) joined the Federal Republic: Brandenburg Brandenburg Brandenburg surrounds the capital city of Berlin and benefits from the latter’s “gin and martini belt”. However, with its numerous lakes and forests it also has several trump cards of its own. With the Hohenzollern castles, and in particular Sanssouci Castle, which is included in the UNESCO World… Read more › , Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Saxony Saxony Meissen may well be a small town but, thanks to its porcelain, is as well known as the state capital Dresden and Leipzig, the trade-fair city. The Free State is one of the most dynamic economic regions in East Germany, in particular in IT; precision watch-making and car-making are typical of this… Read more › , Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia Thuringia The mountains in the Thuringian Forest provide a backdrop for one of Germany’s most beautiful trails, the 168-kilometer long Rennsteig. It is just as much a trademark of the state as its long thin sausages, the historic Wartburg and the Weimar poets Goethe and Schiller. However, Thuringia not only… Read more › . North Rhine-Westphalia North Rhine-Westphalia No state in Germany has more inhabitants than North Rhine-Westphalia, and there is a correspondingly large number of cities: Cologne, with its Gothic cathedral, Bonn, the Federal Republic’s first capital city, Düsseldorf, the fashion-conscious state capital, Aachen, under the rule of Charlemagne… Read more › is the state with the biggest population at around 18 million, while Bavaria Bavaria The “beer state” of Bavaria also produces fine wine in the Franconia region. The Oktoberfest, Neuschwanstein Castle and the magnificent Alpine scenery attract more foreign tourists than does any other federal state. Yet the slogan “Laptop and Lederhose” demonstrates that there is more to Bavaria… Read more › is the largest in terms of surface area at around 70,540 square kilometres. The territory of three federal states is limited to a single metropolitan region: these are the “city states” of Berlin Berlin Once a year, during the Berlinale film festival, the world of the silver screen focuses its attention on Berlin. And the city’s inhabitants are used to global interest. After all, the people of Berlin have lived in a capital city since 1458. However, there is also a shady side to the city’s history… Read more › , Bremen Bremen The Hanseatic city of Bremen arose through classic maritime trading, in particular with coffee. In the smallest of the federal states (divided into the city of Bremen, and Bremerhaven, some 60 kilometers to the north) the port accounts for every fifth job. The largest private employer, however, is… Read more › /Bremerhaven and Hamburg Hamburg In the city and state of Hamburg it is the port that is the power-house of the economy, though with Airbus, Otto Versand and Beiersdorf also located here, this is not immediately apparent. The tanker terminals, mean that almost all the major oil-refining companies are represented in the port. For… Read more › .
A journey through Germany’s states

The third-largest state is located in south-west Germany, bordering France and Switzerland. The state capital is Stuttgart. With more than eleven million inhabitants, Baden-Württemberg is famous for its holiday regions such as the Black Forest and cultural centres like Heidelberg (photo), not to mention its economic strength. Baden-Württemberg is Germany’s number one export Export Germany is one of the leading export nations. In 2022 it exported goods and services valued at some 1,576 billion Euros. The balance of foreign trade fort he year posted a surplus of 81 billion Euros. Germany has above all the strong performance of its industry to thank for its strength in exports… Read more › state and home to both large, internationally renowned corporations and smaller global market leaders - so-called “hidden champions”.

In the south-east of Germany lies the largest federal state with its panorama of the Alps to the south. Germany’s highest mountain is also to be found in Bavaria Bavaria The “beer state” of Bavaria also produces fine wine in the Franconia region. The Oktoberfest, Neuschwanstein Castle and the magnificent Alpine scenery attract more foreign tourists than does any other federal state. Yet the slogan “Laptop and Lederhose” demonstrates that there is more to Bavaria… Read more › : the Zugspitze. Each year, the state capital Munich (photo) hosts the world’s biggest beer festival, the Oktoberfest. With a population of over 13 million, Bavaria is also home to Bayern Munich, Germany’s most successful football club, and is one of the country’s economically strongest regions.

As a “city state”, the capital of Germany is also a federal state in its own right - like Hamburg Hamburg In the city and state of Hamburg it is the port that is the power-house of the economy, though with Airbus, Otto Versand and Beiersdorf also located here, this is not immediately apparent. The tanker terminals, mean that almost all the major oil-refining companies are represented in the port. For… Read more › and Bremen Bremen The Hanseatic city of Bremen arose through classic maritime trading, in particular with coffee. In the smallest of the federal states (divided into the city of Bremen, and Bremerhaven, some 60 kilometers to the north) the port accounts for every fifth job. The largest private employer, however, is… Read more › . Nearly four million people live in the city, which was divided into two parts until the Berlin Wall fell in November 1989. Berlin has landmarks that are famous worldwide, such as the Brandenburg Brandenburg Brandenburg surrounds the capital city of Berlin and benefits from the latter’s “gin and martini belt”. However, with its numerous lakes and forests it also has several trump cards of its own. With the Hohenzollern castles, and in particular Sanssouci Castle, which is included in the UNESCO World… Read more › Gate, the Reichstag (photo) - the seat of the German Bundestag - and Checkpoint Charlie at the former internal German border crossing. The capital offers rich cultural diversity, including the Museum Island in the heart of the city - a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

This federal state surrounds the vibrant capital of Berlin Berlin Once a year, during the Berlinale film festival, the world of the silver screen focuses its attention on Berlin. And the city’s inhabitants are used to global interest. After all, the people of Berlin have lived in a capital city since 1458. However, there is also a shady side to the city’s history… Read more › . A sparsely populated region with forests and some 3,000 lakes, it attracts numerous city dwellers at the weekend. Around 2.5 million people live in Brandenburg Brandenburg Brandenburg surrounds the capital city of Berlin and benefits from the latter’s “gin and martini belt”. However, with its numerous lakes and forests it also has several trump cards of its own. With the Hohenzollern castles, and in particular Sanssouci Castle, which is included in the UNESCO World… Read more › , more than a million fewer than in Berlin. With its world-famous Sanssouci Palace (photo), the state capital Potsdam directly borders Germany’s capital.

This “city state” is the smallest federal state and is made up of two cities: Bremen Bremen The Hanseatic city of Bremen arose through classic maritime trading, in particular with coffee. In the smallest of the federal states (divided into the city of Bremen, and Bremerhaven, some 60 kilometers to the north) the port accounts for every fifth job. The largest private employer, however, is… Read more › and Bremerhaven, located directly on the North Sea coast around 60 kilometres to the north. It has a population of some 700,000. The Bremen Town Musicians (photo) are a city landmark: a statue in the city commemorates the adventures of the donkey, cat and cockerel - the characters in the folk tale of the same name.

The Hanseatic city of Hamburg Hamburg In the city and state of Hamburg it is the port that is the power-house of the economy, though with Airbus, Otto Versand and Beiersdorf also located here, this is not immediately apparent. The tanker terminals, mean that almost all the major oil-refining companies are represented in the port. For… Read more › is Germany’s second-largest city and one of Germany’s three city states. With a population of nearly two million, it is Germany’s biggest seaport - a gateway to the world. A longstanding tradition of trade and commerce is still very much in evidence in this cosmopolitan northern metropolis. The Elbphilharmonie concert hall (photo) has recently become established as a new city landmark, offering concerts, fascinating architecture and spectacular views of the city and harbour.

After the Second World War, Hesse Hesse Frankfurt am Main is really the only city in Germany that has an international feel to it: The tallest buildings in Germany, the largest airport and the most banks in continental Europe (including the European Central Bank). And the list of superlatives does not stop there; for example, there… Read more › ’s finance and trade metropolis Frankfurt am Main was a possible candidate for the capital of the Federal Republic of Germany, though instead this honour went initially to Bonn and then, after reunification, to Berlin Berlin Once a year, during the Berlinale film festival, the world of the silver screen focuses its attention on Berlin. And the city’s inhabitants are used to global interest. After all, the people of Berlin have lived in a capital city since 1458. However, there is also a shady side to the city’s history… Read more › . With its skyline, stock exchange and Germany’s biggest airport, Frankfurt (photo) still defines the image of Hesse to this day, though the state capital is nearby Wiesbaden. With a population of over six million, Hesse is also one of the most densely forested regions in Germany.

Located in the north-west of Germany and with a population of 1.6 million, the most sparsely populated federal state is a scenic paradise: with more than 2,000 lakes and 350 kilometres of Baltic coastline, it is one of the country’s most popular travel destinations. Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania is also home to Germany’s largest island, Usedom. The state capital is Schwerin, where the imposing Schwerin Palace (photo) with its 1,000-year history has been the seat of the state parliament since 1990.

Germany’s second-largest state in terms of surface area extends from the East Frisian islands in the North Sea such as Borkum and Norderney to the Harz mountains. With a population of some eight million, the state has an economy that is dominated by tourism and agriculture. The automotive industry is also a key factor, while important trade fairs Trade fairs With 150 international trade fairs, Germany is a leading international marketplace for goods and commodities. Major events include the annual Hannover Messe, which is regarded as an industry showcase, and also IAA Mobility, which is organised by the German Association of the Automotive Industry. In… Read more › are held in the state capital of Hanover (photo).

Germany’s most populous state combines such diverse regions as the Ruhr, which was once defined by its coal mining industry, and the Rhineland, which features Cologne (photo) - a city of over a million inhabitants - and state capital Dusseldorf at its heart. North Rhine-Westphalia North Rhine-Westphalia No state in Germany has more inhabitants than North Rhine-Westphalia, and there is a correspondingly large number of cities: Cologne, with its Gothic cathedral, Bonn, the Federal Republic’s first capital city, Düsseldorf, the fashion-conscious state capital, Aachen, under the rule of Charlemagne… Read more › is in transition, too: in this state with a population of 18 million, research and culture are now taking the place of coal mining. Up until reunification in 1990, the city of Bonn near Cologne was the capital of the Federal Republic of Germany.

This state in the country’s south-west is the number one wine-growing state in Germany: six of Germany’s 13 wine-growing regions are to be found in Rhineland-Palatinate Rhineland-Palatinate The Rhine valley between Bingen and Koblenz, a gem that is for the most part located in Rhineland-Palatinate, is a key item on the UNESCO World Cultural Heritage List. A center of wine and sparkling wine production, the state is also referred to as “Wineland-Palatinate”. Yet from an early date it… Read more › , including the largest of these - Rhine Hesse Hesse Frankfurt am Main is really the only city in Germany that has an international feel to it: The tallest buildings in Germany, the largest airport and the most banks in continental Europe (including the European Central Bank). And the list of superlatives does not stop there; for example, there… Read more › (photo). The Romans left their mark on the region more than 2,000 years ago; nowhere else in Germany are there more Roman monuments. Rhineland-Palatinate has a population of some four million and its capital is Mainz.

It was not until 1957 that Saarland Saarland Saarbrücken’s film festival for German-speaking up-and-coming talent has been the launching pad for many a career, as Franka Potente and Til Schweiger have proved. The state has over the last 200 years changed nationality eight times and the French influence is highly evident. Mining is now no… Read more › became the tenth federal state of the Federal Republic of Germany, having initially been a semi-autonomous state with close ties to France after the Second World War. The state’s location within the greater European SaarLorLux region, which extends across parts of Germany, France, Luxembourg and Belgium, significantly influences the lives of its nearly one million inhabitants. Saarbrücken (photo) is the state capital of Germany’s smallest territorial state.

Boasting more than 1,000 years of history, the Free State of Saxony Saxony Meissen may well be a small town but, thanks to its porcelain, is as well known as the state capital Dresden and Leipzig, the trade-fair city. The Free State is one of the most dynamic economic regions in East Germany, in particular in IT; precision watch-making and car-making are typical of this… Read more › is situated on the border to Poland and the Czech Republic. With a population of four million, the state is a key business hub in eastern Germany but also attracts numerous visitors every year to the state capital Dresden (photo) - known as “Florence on the River Elbe” - as well as to the economic and cultural metropolis of Leipzig and the Ore Mountains.

With six UNESCO World Cultural Heritage sites, this state in the middle of Germany boasts one of the highest numbers of world heritage sites. These include the Bauhaus Bauhaus Bauhaus (1919–1933) is considered to be the most famous art, design and architecture college of Classic Modernism. Founded by Walter Gropius it was located in Weimar and later in Dessau. Bauhaus artists and architects created a new, clear, contemporary formal language, much of which still exerts an… Read more › in Dessau, the memorials to Martin Luther in Eisleben and Wittenberg and the historic centre of Quedlinburg (photo). With a population of around two million, the state is also an important centre for the chemical industry and European chip production. The state capital is Magdeburg.

Known as the “land between the seas”, Schleswig-Holstein Schleswig-Holstein The most feared mythical figure in Schleswig-Holstein is “Blanker Hans”, who stands for the destructive forces of the sea. After all, the most northern of the federal states is bordered by two seas, the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. Since time immemorial, ship-building and fishing have been… Read more › is situated between the North Sea in the west and the Baltic Sea in the east, and borders Denmark in the north. Germany’s northernmost federal state has a population of almost three million and its capital is Kiel. With islands such as Sylt (photo), the state is among the most popular holiday regions. Stretching from the Netherlands to Germany and Denmark, the Wadden sea World Heritage Site is an important landmark.

This state is geographically located at the heart of Germany and was where Goethe, Bach and Luther lived: the composer Johann Sebastian Bach was born in Eisenach, the poet Johann Wolfgang von Goethe lived for many years in Weimar (photo) and the reformer Martin Luther translated the New Testament of the Bible into German at Wartburg Castle. The state has a population of over two million and its capital is Erfurt.


